About the system
- ensures the safety of shunting and hump operations in mainline and industrial railway stations and yards.
- transmits route jobs and allowed speed limits, including stop commands, to engines via radio.
- prevents SPAD and speed limit violations.
- supervises the movements and locations of engines using satellite navigation with results displayed on graphical screen and trips recorded in text and graphical form.
- is interfaced and communicates with all types of electrical and marshaling interlocking systems, station-level information and planning systems, computer-based onboard control systems.
- is deployed in the following stations: Solnechnaya, Avtovo, Orekhovo-Zuevo, Sochi, Adler, Imeretinsky Resort, Cheliabinsk Glavny, Bekasovo Sortirovochnoye, Luzhskaya (shunting system, Northern, Oil and Southern yards).
Awards and certificates
Aims and goals

Unmanned technologies
Safety
- non-observance of signals;
- violation of voice communication rules;
- movement without foreman's command;
- poor brake control;
- poor knowledge of the station's technological instructions;
- sleeping in locomotive;
- poor signal visibility;
- speed limit violation;
- erroneous perception of adjacent track's signal as own track's signal;
- foreman's command to driver containing a wrong locomotive identification number;
- damage to wagons during coupling due to shunting master's error or misperception of command by driver;
- erroneous setting of movement direction.
Dynamic modelling and prevention of accidents using MALS
Monitoring
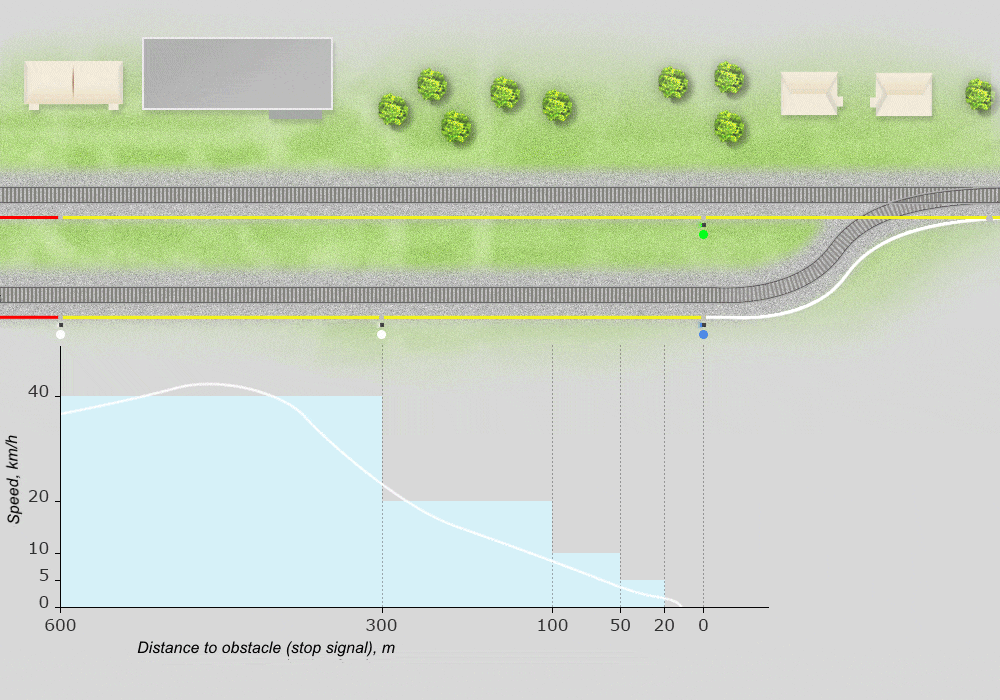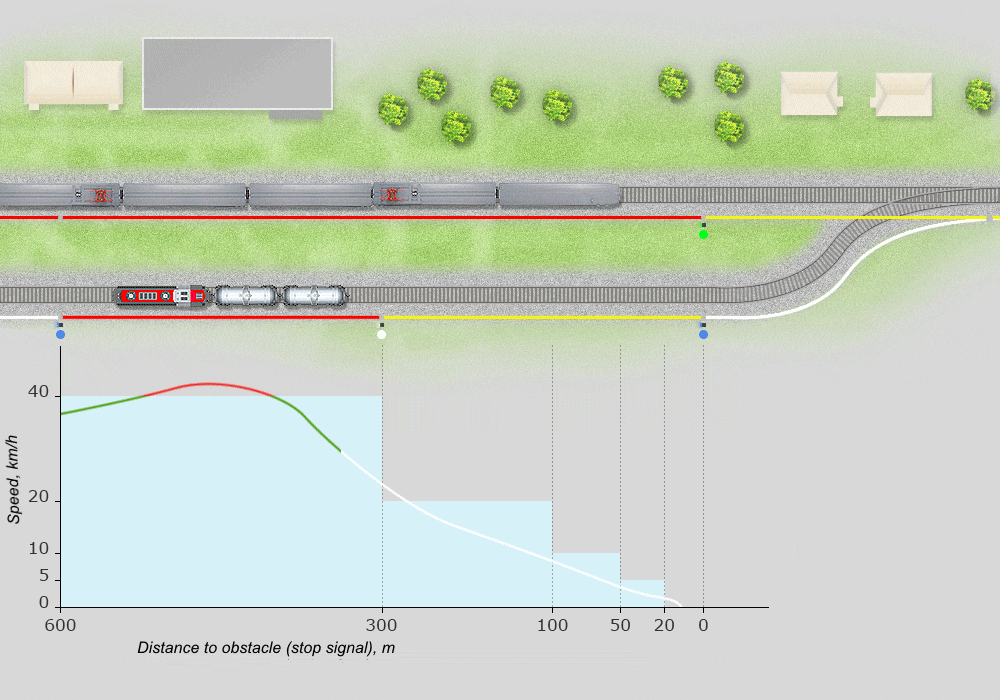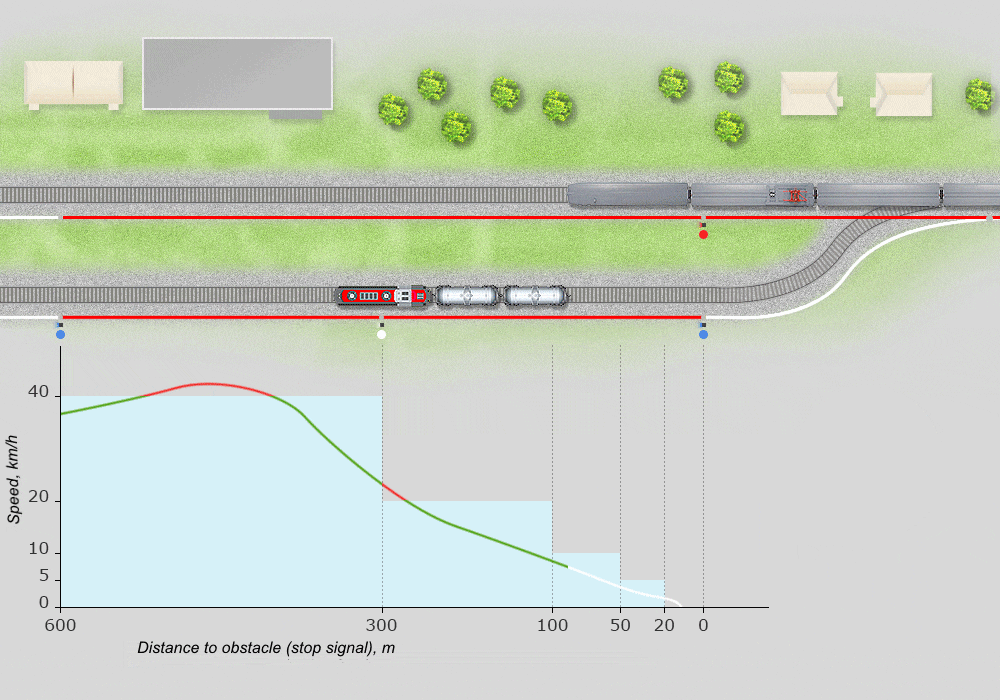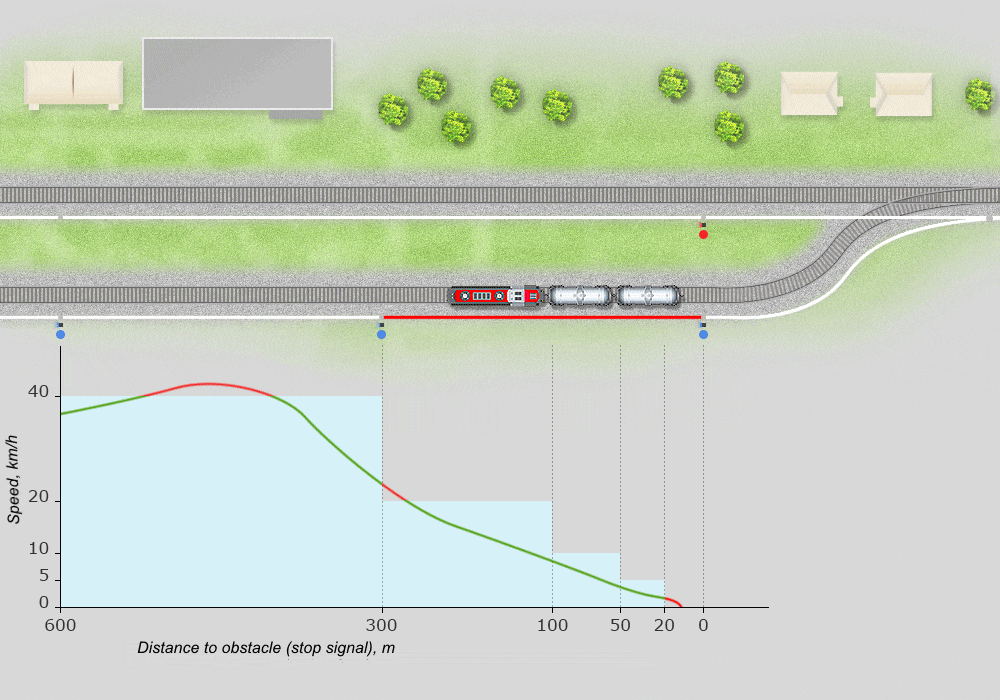
Supervises the locations and movements of locomotives by means of satellite navigation and station-based automation devices with graphical display of information.
Identifies and visually indicates operations and speed violations, threats to traffic safety, violations of instructions and norms. Enables transmission of current information, graphical and text records to remote terminals via wire and wireless channels.
Example of speed gauge reflecting the implementation of a shunting route:
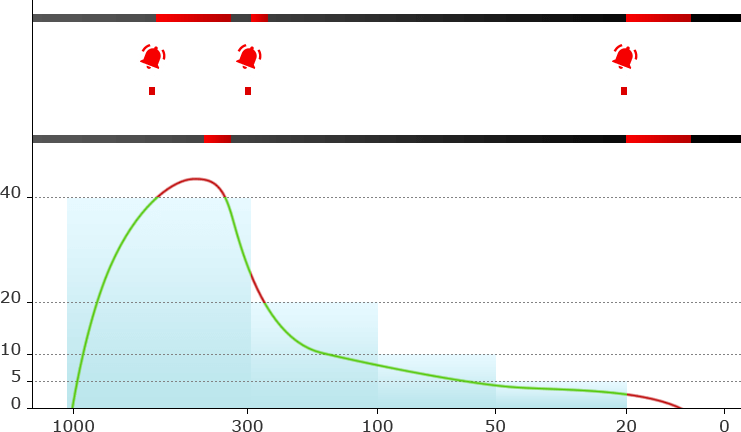
Analytics
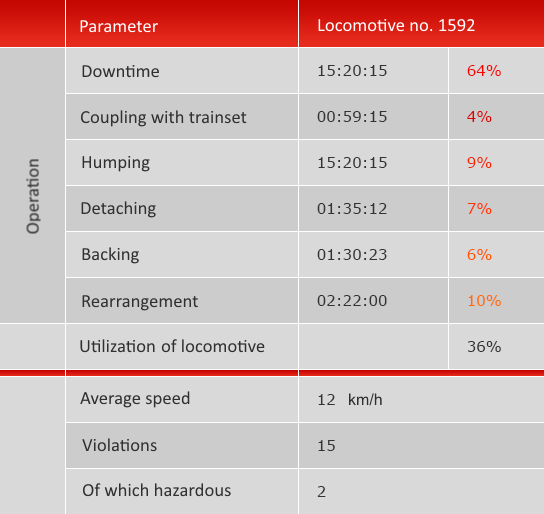
Based on archive data, MALS generates a statistical report on the operation of locomotives equipped with the system's devices, that contains indicators that allow evaluating the efficiency of shunting engine operation, identifying bottlenecks in the station and hump operation process, pinning down process discipline violations by train crew members. The significant advantage of the MALS statistics is the fully automated acquisition of information that ensures high integrity of locomotive operation indicators.
Economic efficiency

Unmanned technologies
MALS provides a wide range of opportunities for application and further development of unmanned technologies of railway rolling stock control during shunting operations in stations, while completely observing traffic safety requirements.
The driver can set the speed that will be automatically implemented by the locomotive using the MALS facilities. The driver's function in this case comes down to observing the progress of operations.
In the driverless mode all the parameters required for the performance of shunting operations are set at the station duty officer's workstation, and the locomotive automatically performs the required operation (approach to trainset, coupling with trainset, humping, detaching).
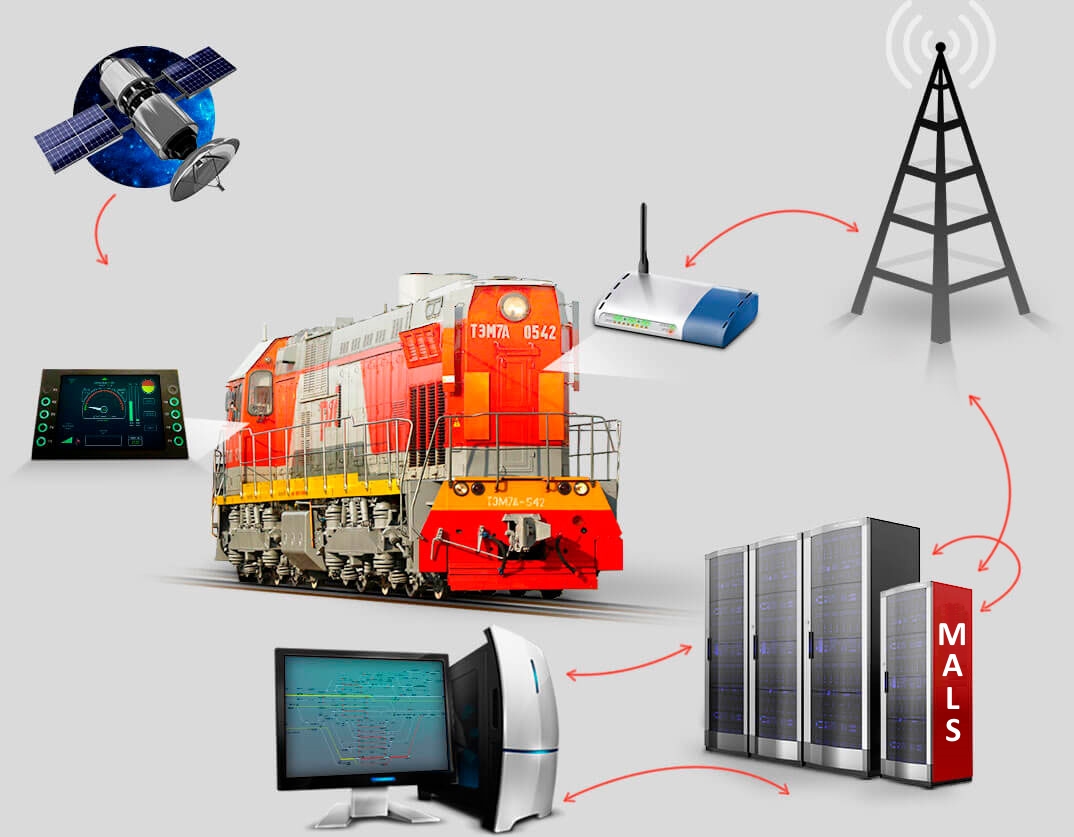
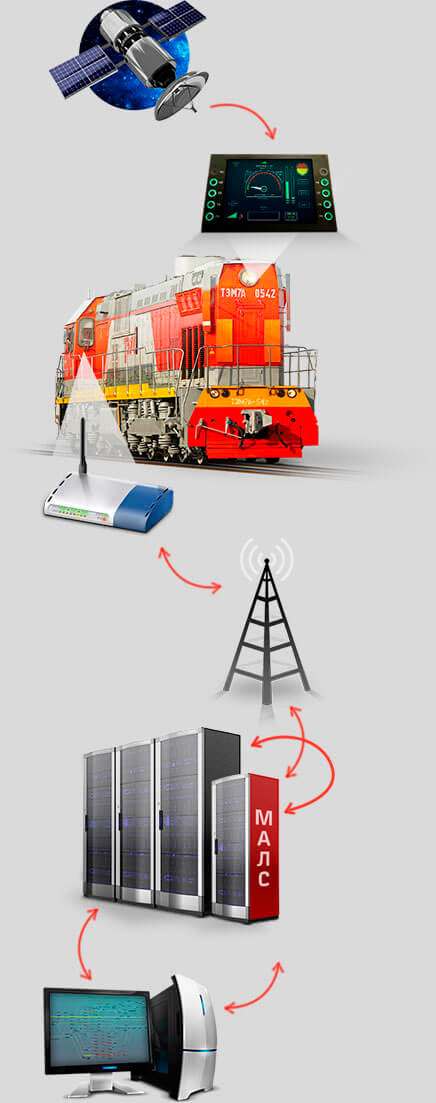
How MALS works
Technical failures analysis
GLONASS/GPS
ONBOARD EQUIPMENT and driver's workstation
RADIO TOWER
ONBOARD RADIO STATION
CBI/IXL
STATION DUTY OFFICER'S WORKSTATION
MALS station-based control computer
System functions
- Delivery of commands to stop the locomotive before restrictive signals;
- Supervision of shunting engines' speed as per the station's instructions, including during distribution of wagons from the hump;
- Supervision of shunting engines' location and movement along the tracks and in the yards of the station using satellite navigation;
- Target backing a trainset into dead-end siding;
- Recording and logging of the operation of onboard, station-based devices and radio communication facilities;
- Fully automated generation of statistical records of locomotive operating performance (with no manual input).
Contacts
- g.zuev@vniias.ru
 Russian
Russian